Hair loss in
women
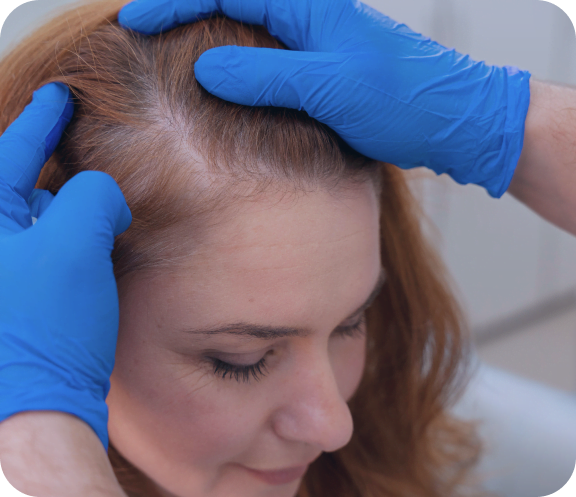
Admit it — when you see or hear hair loss advertisements, it’s often about men losing their hair. Hair products like creams, shampoos, and supplements are all geared toward male pattern baldness. However, many do not realize that women also suffer from thinning hair.
Often, we associate male pattern baldness with aging or genetics. However, what causes hair loss for women can sometimes be hard to explain. At times, female baldness is a symptom of a more serious problem.
It is embarrassing to experience hair loss. That is why most women are quick to search for what causes their hair to fall. Usually, they may change their diets and consult their doctor immediately. Also, they often buy special shampoos to reverse the effects of their hair loss problem. However, when all solutions fail, they start to look for wigs.
The Hair Transplant Center – New Jersey offers solutions for women’s hair loss. We are conveniently located to serve the areas of Bergen County, Northern, Central, and South New Jersey.